The rising regulatory focus on modern slavery
Modern slavery, a pervasive human rights violation, remains a global crisis affecting millions of people. According to the Global Slavery Index 2023, approximately 50 million individuals were living in modern slavery, with 28 million in forced labor and 22 million in forced marriage. This human rights issue operates in the shadows of complex supply chains, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations and undermining economic progress. These staggering figures underscore the urgency of addressing this issue.
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in regulatory initiatives aimed at eradicating modern slavery. Governments, international organizations, and civil society groups are increasingly collaborating to develop and enforce legislation that holds businesses accountable for ensuring their operations and supply chains are free from modern slavery.
# I. What is modern slavery?
Anti-Slavery International defines modern slavery as a situation “when an individual is exploited by others, for personal or commercial gain. Whether tricked, coerced, or forced, they lose their freedom.” Modern slavery is an umbrella term for forced labor, child labor, human trafficking, and other slavery-like practices.
Modern slavery not only inflicts immense suffering on victims but also poses significant risks to businesses. These risks include reputational damage, legal liabilities, operational disruptions, and investor divestment. The growing consumer and investor demands for ethical sourcing further underscores the need for businesses to eradicate modern slavery.
# II. What are the key regulations addressing modern slavery?
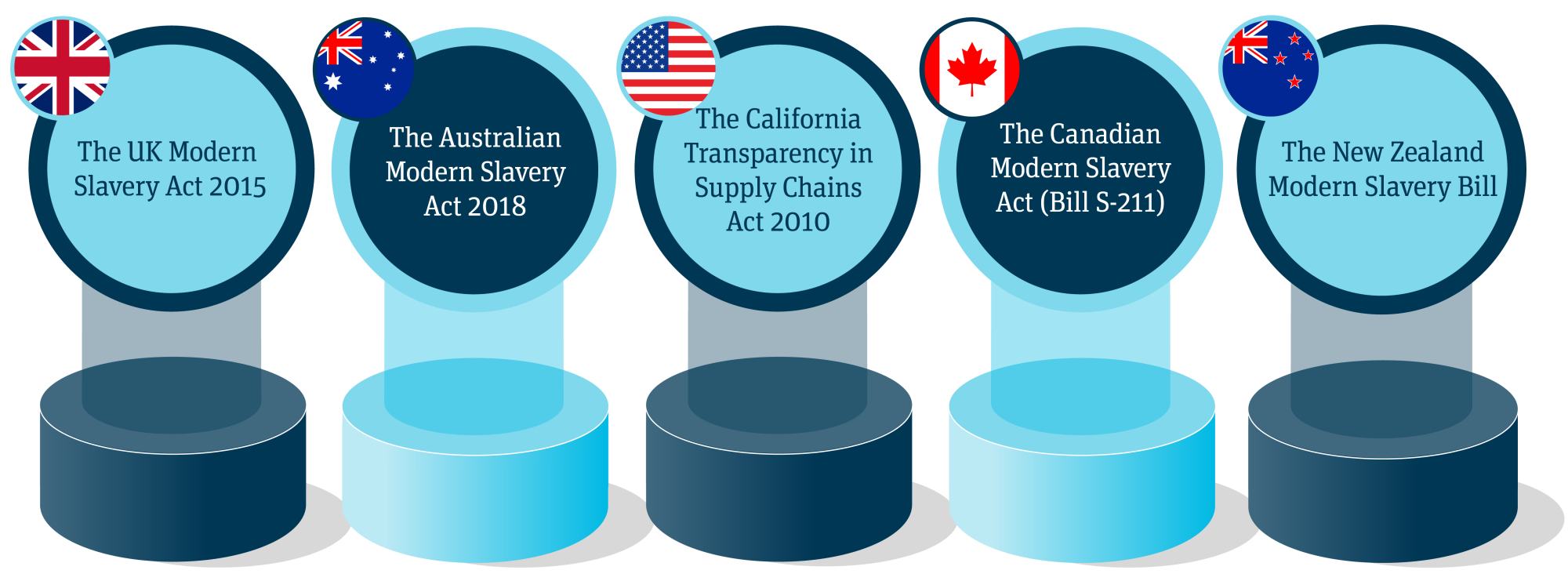
- The UK Modern Slavery Act 2015: the world’s first regulation tacking modern slavery mandates companies with a global turnover exceeding GBP 36 million to publish annual statements detailing steps taken to address modern slavery risks in their operations and supply chains.
- The Australian Modern Slavery Act 2018: mirroring the UK Act, this legislation requires large businesses to report annually on their actions to assess and manage modern slavery risks.
- The California Transparency in Supply Chains Act 2010: requires retailers and manufacturers operating in California to disclose their efforts to eradicate slavery and human trafficking from their supply chains.
- The Canadian Modern Slavery Act (Bill S-211): mandates companies producing, selling, or importing goods in Canada to report annually on their efforts to prevent and reduce the risk of forced labor and child labor in their supply chains.
- The New Zealand Modern Slavery Bill: currently being developed, it will require certain organizations to assess and report on the risks of modern slavery in their operations and supply chains.
# III. How do modern slavery risks impact the global ESG landscape?
The escalating regulatory focus on modern slavery has transformed the global ESG landscape. Recognizing both its financial and impact materiality, investors and stakeholders are increasingly demanding corporate accountability on this issue. Companies with robust ESG performance, particularly in mitigating modern slavery risks, are perceived as more sustainable and attractive investments.
Moreover, the proliferation of ESG risk data, ratings, and indices, which assess companies' performance on ESG criteria, has amplified the importance of modern slavery as a key indicator. Strong performance in this area can significantly influence investor decisions and capital allocation.
The way forward
Despite progress, eradicating modern slavery remains challenging. Complex global supply chains, inadequate enforcement mechanisms, and limited resources hinder the effective implementation of regulations. The informal nature of many sectors where modern slavery thrives further complicates detection and remediation efforts.
However, the rising regulatory focus on modern slavery signifies a turning point in the global fight against this egregious human rights violation. Its importance lies not only in the moral imperative to protect human dignity but also in the economic benefits of sustainable and ethical business practices. As modern slavery increasingly becomes a focal point in ESG evaluations, it will continue to shape the global business landscape, driving companies toward greater transparency, accountability, and responsible conduct.
Want to learn more about how RepRisk solutions address modern slavery?
Contact your Account Manager or our Client Services Team (support@reprisk.com)
Copyright 2024 RepRisk AG. All rights reserved. RepRisk AG owns all intellectual property rights to this report. This information herein is given in summary form and RepRisk AG and/or the third party contributors to this report make no representation or warranty that any data or information supplied to or by it or them is complete or free from errors, omissions, or defects. Without limiting the foregoing, in no event shall RepRisk AG and/or the third party contributors to this report have any liability (whether in negligence or otherwise) to any person in connection with the information contained herein. Any reference to or distribution of this report must include a link to the content to provide sufficient context. The information provided in this presentation does not constitute an offer or quote for our services or a recommendation regarding any investment or other business decision, and is not intended to constitute or to be used as a substitute for legal, tax, accounting, or other professional advice. Please note that the information may have become outdated since its publication. Should you wish to obtain a quote for our services, please contact us.



